Thermal images
The term "thermography" describes an imaging process in which the thermal infrared radiation of objects is registered using a thermal imaging camera or a thermal scanner.
If additional information is included (e.g. material properties, geometry of the surroundings, atmospheric influences), the surface temperatures of the recorded objects can be derived from the radiation data.
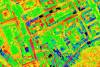
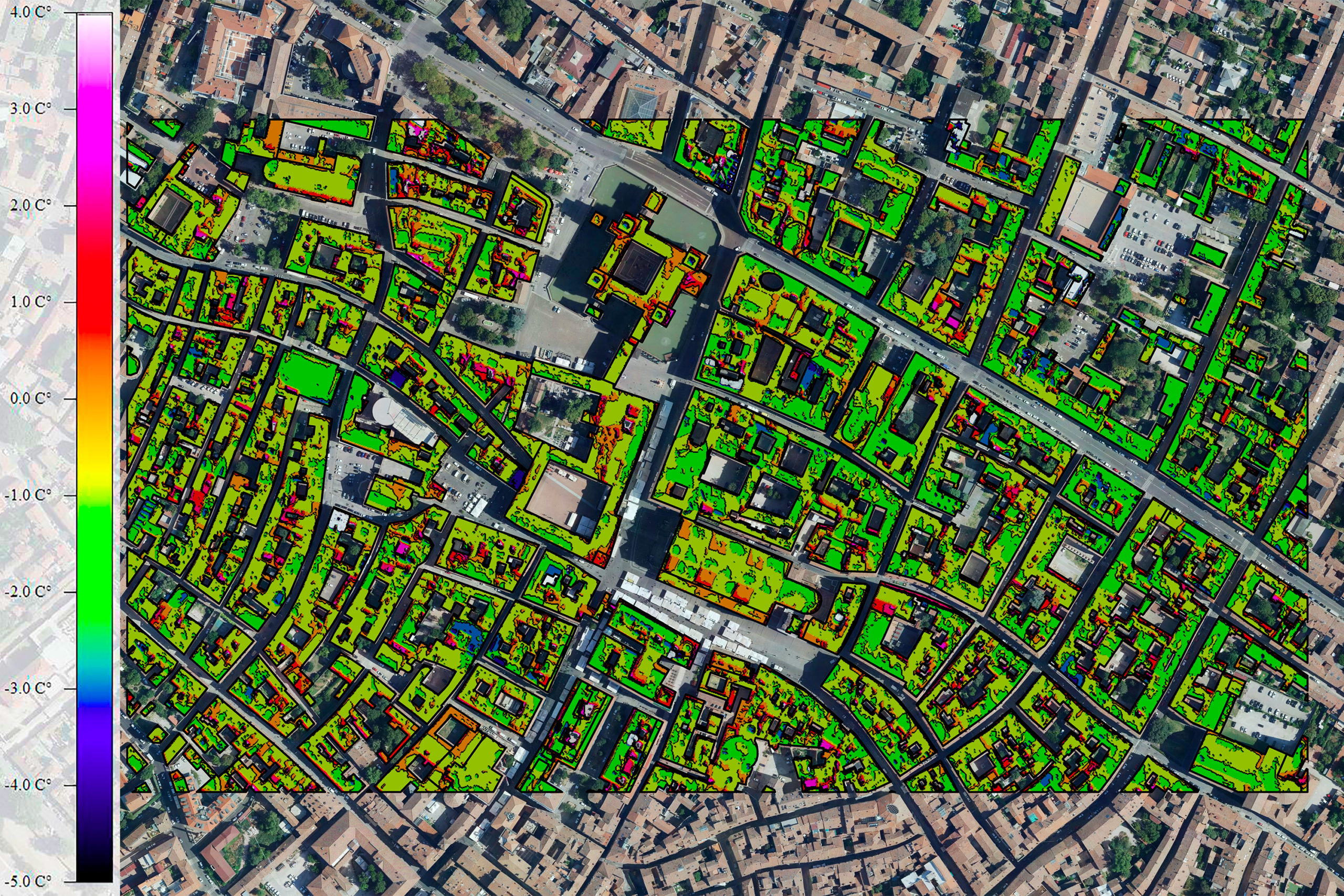
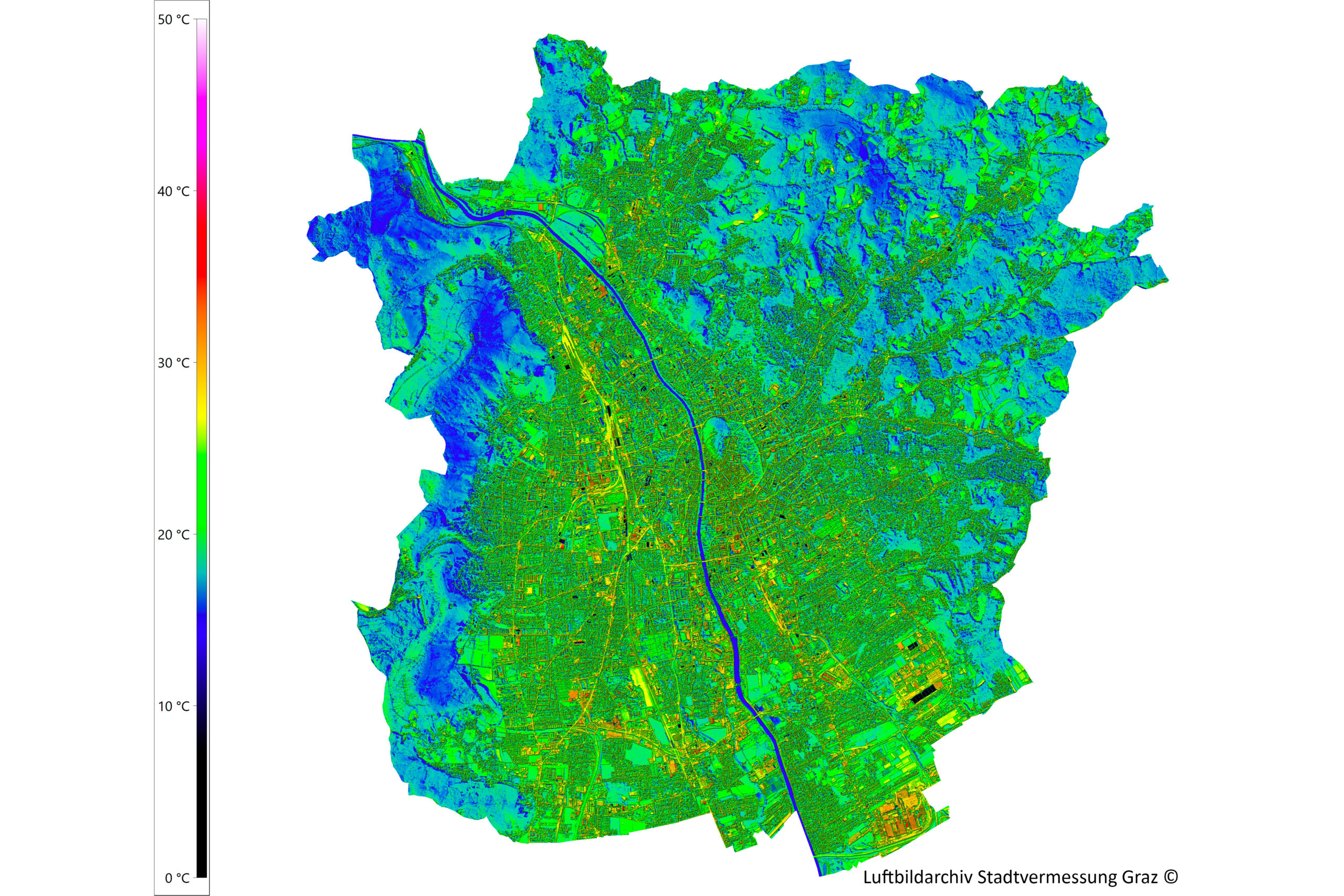
Thermal images can be evaluated and visualized using various methods. As infrared radiation is invisible to the human eye, it is made visible using color scales that are easy to interpret.
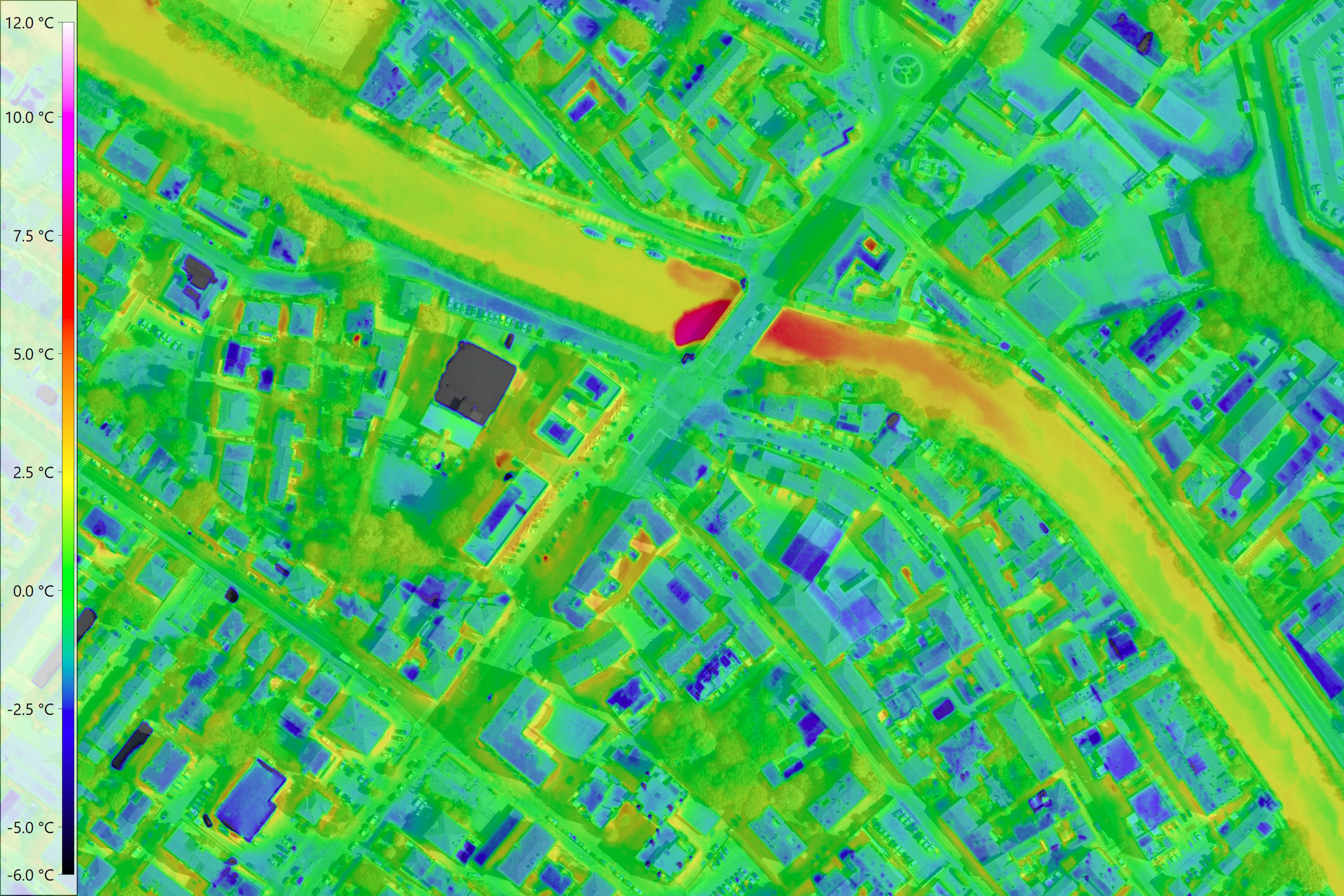
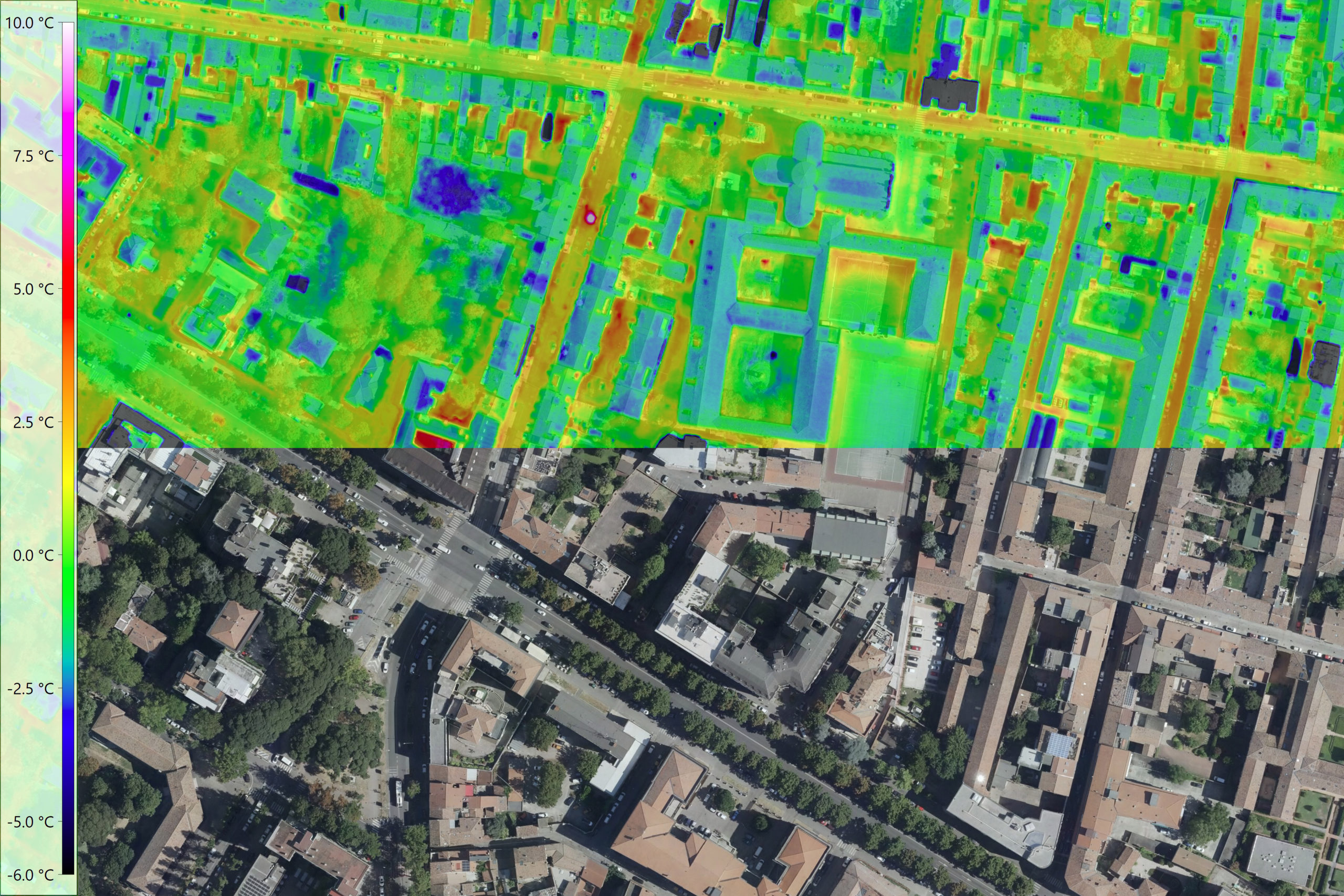
Today, thermographic systems are widely used in construction technology, medicine, research, industrial production and many other areas of everyday life. Particularly in the context of the advancing Global warming airborne thermography is becoming increasingly important. Climate change is increasing the likelihood of hot days and longer periods of heat. Densely built-up or sealed areas heat up particularly strongly. In cities and industrial zones in particular, "Heat islands" form. Such hot spots can be identified with the help of large-scale thermal scanner flights. The knowledge gained from this provides an important planning basis for the climate change adaptation strategy.
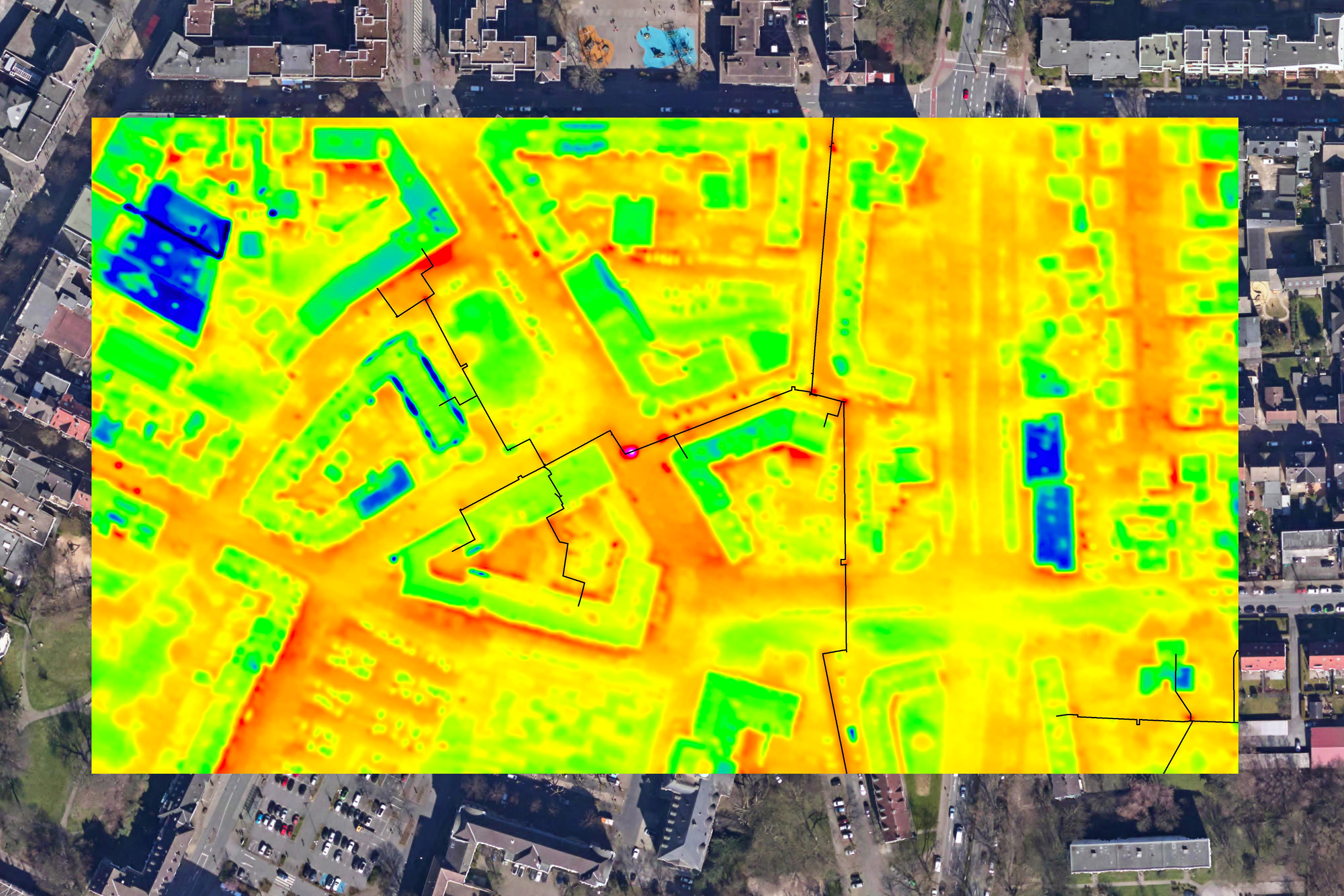
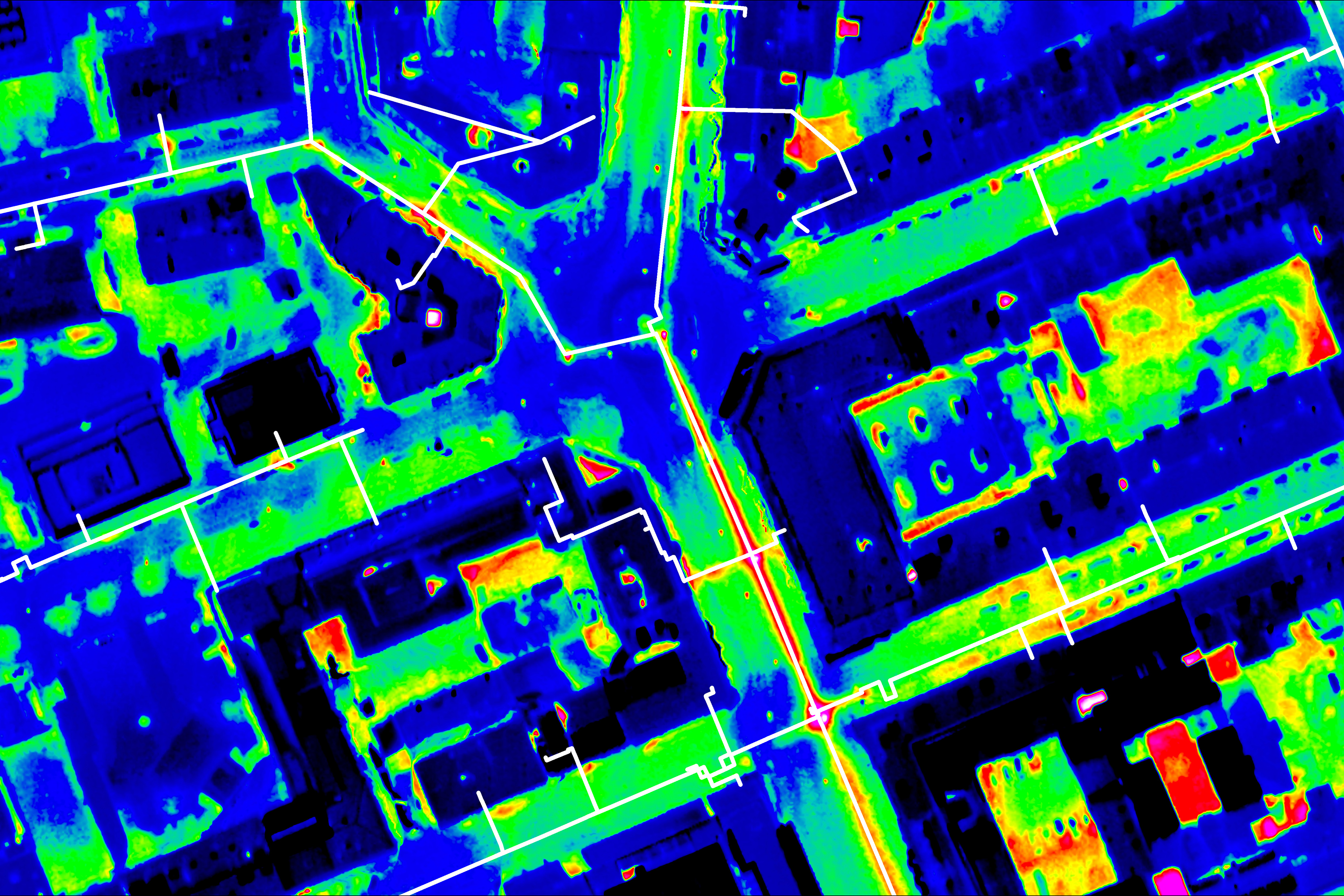
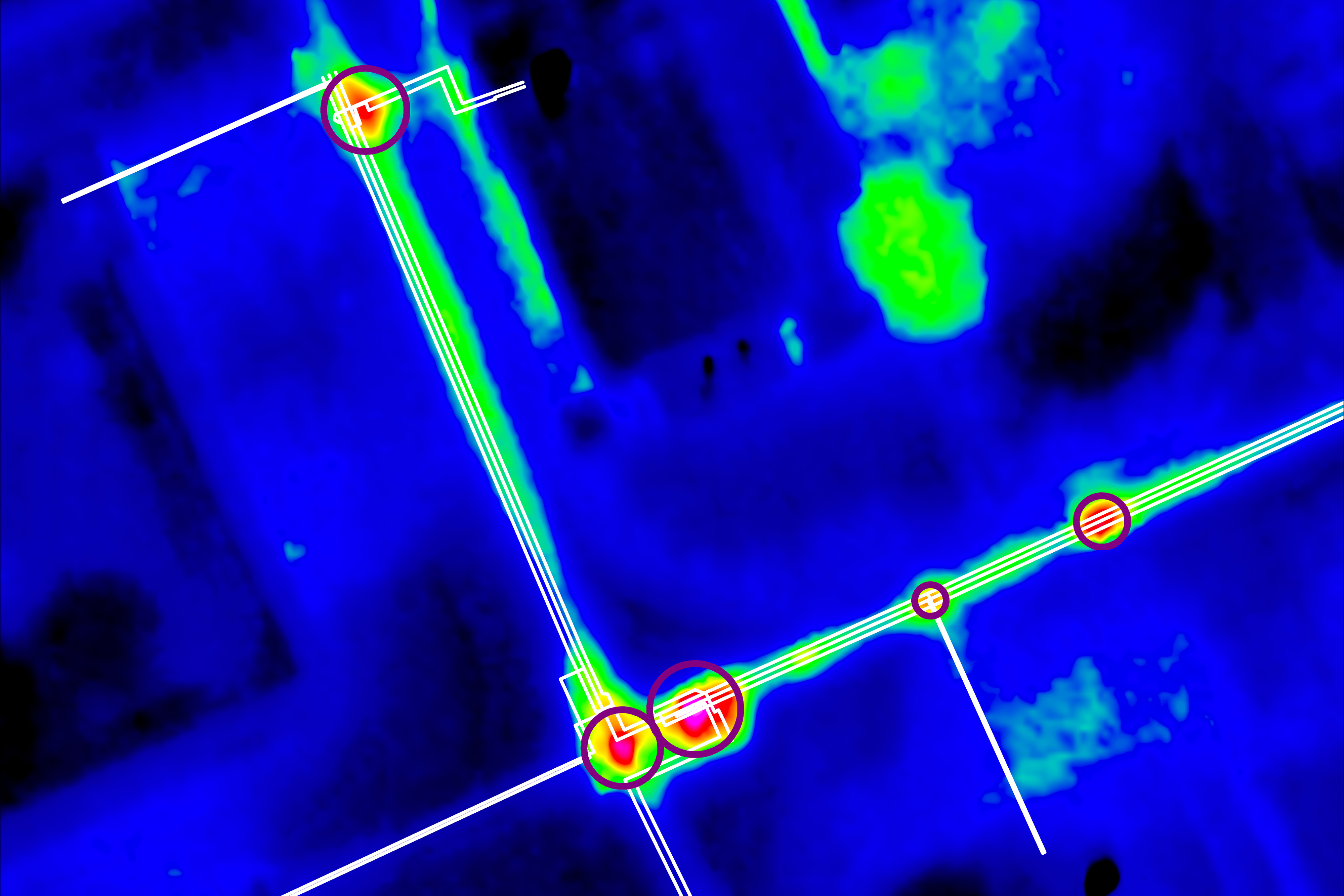
Another valuable application scenario is the Inspection of district heating networks. In order to be able to detect leaks or leaking points, an aerial survey is carried out at night during the cold season. This is when the temperature difference to the surroundings is great and the district heating pipes become very visible. The thermal images are available just a few days after the aerial survey and are analyzed, interpreted and clearly displayed by us. This means that conspicuous areas can be identified quickly and any necessary repairs can be carried out promptly.